GPIO, Input & Output GUI panel using Tkinter
The article guides you through Designing a Graphical panel to control all the 21 GPIO’s of Raspberry Pi as an Input or Output Pin.
In this tutorial we will be Designing a Graphical panel through which we will be able to control all the 21 GPIO's of Raspberry Pi as an Input or Output Pin.
Credits for the program - scotty3785, Original code link - click here
Step 1 - Programming the Raspberry Pi
Step 2 - Running the program and Understanding the GUI panel
- Open the python IDLE in Raspberry Pi and create a new Python file and enter the following code.
#This code has been published by Robu.in
#visit https://robu.in for more information
import sys
if(sys.version_info[0]<3):
from Tkinter import *
else:
from tkinter import *
import RPi.GPIO as pi
import math
#import tkSimpleDialog
class LED(Frame):
"""A Tkinter LED Widget.
a = LED(root,10)
a.set(True)
current_state = a.get()"""
OFF_STATE = 0
ON_STATE = 1
def __init__(self,master,size=10,**kw):
self.size = size
Frame.__init__(self,master,width=size,height=size)
self.configure(**kw)
self.state = LED.OFF_STATE
self.c = Canvas(self,width=self['width'],height=self['height'])
self.c.grid()
self.led = self._drawcircle((self.size/2)+1,(self.size/2)+1,(self.size-1)/2)
def _drawcircle(self,x,y,rad):
"""Draws the circle initially"""
color="red"
return self.c.create_oval(x-rad,y-rad,x+rad,y+rad,width=rad/5,fill=color,outline='black')
def _change_color(self):
"""Updates the LED colour"""
if self.state == LED.ON_STATE:
color="green"
else:
color="red"
self.c.itemconfig(self.led, fill=color)
def set(self,state):
"""Set the state of the LED to be True or False"""
self.state = state
self._change_color()
def get(self):
"""Returns the current state of the LED"""
return self.state
## Future Functionality
##class gpioEdit(tkSimpleDialog.Dialog):
## """Dialog to be expanded to support advanced gpio features like
## - Pull Up / Pull Down Resistor Config
## - Debounce"""
## def __init__(self, master,gpio):
## top = self.top = Toplevel(master)
## if gpio.isInput():
## title = "Edit Input: %s" %(str(gpio.name))
## else:
## title = "Edit Output: %s" %(str(gpio.name))
## l = Label(top,text=title)
## b = Button(top, text="Submit", command=self.submit)
##
## l.grid(row=0)
## b.grid(row=1)
##
## def submit(self):
## print("Submitted")
## self.top.destroy()
class GPIO(Frame):
"""Each GPIO class draws a Tkinter frame containing:
- A Label to show the GPIO Port Name
- A data direction spin box to select pin as input or output
- A checkbox to set an output pin on or off
- An LED widget to show the pin's current state
- A Label to indicate the GPIOs current function"""
gpio_modes = ("Passive","Input","Output")
def __init__(self,parent,pin=0,name=None,**kw):
self.pin = pin
if name == None:
self.name = "GPIO %02d" % (self.pin)
Frame.__init__(self,parent,width=150,height=20,relief=SUNKEN,bd=1,padx=5,pady=5)
##Future capability
##self.bind('<Double-Button-1>', lambda e, s=self: self._configurePin(e.y))
self.parent = parent
self.configure(**kw)
self.state = False
self.cmdState = IntVar()
self.Label = Label(self,text=self.name)
self.mode_sel = Spinbox(self,values=self.gpio_modes,wrap=True,command=self.setMode)
self.set_state = Checkbutton(self,text="High/Low",variable=self.cmdState,command=self.toggleCmdState)
self.led = LED(self,20)
self.Label.grid(column=0,row=0)
self.mode_sel.grid(column=1,row=0)
self.set_state.grid(column=2,row=0)
self.current_mode = StringVar()
self.led.grid(column=3,row=0)
self.set_state.config(state=DISABLED)
function = self.getPinFunctionName()
if function not in ['Input','Output']:
self.mode_sel.delete(0,'end')
self.mode_sel.insert(0,function)
self.mode_sel['state'] = DISABLED
## def _configurePin(self, y):
## """Future capability to setup pull up/down"""
## new = gpioEdit(self.parent,self)
def isInput(self):
"""Returns True if the current pin is an input"""
return (self.mode_sel.get() == "Input")
def setMode(self):
"""Sets the GPIO port to be either an input or output
Depending on the value in the spinbox"""
if (self.mode_sel.get() == "Input"):
self.set_state.config(state=DISABLED)
pi.setup(self.pin,pi.IN)
elif (self.mode_sel.get() == "Passive"):
self.set_state.config(state=DISABLED)
pi.cleanup(self.pin)
else:
self.set_state.config(state=NORMAL)
pi.setup(self.pin,pi.OUT)
self.updateInput()
def getPinFunctionName(self):
pin = self.pin
functions = {pi.IN:'Input',
pi.OUT:'Output',
pi.I2C:'I2C',
pi.SPI:'SPI',
pi.HARD_PWM:'HARD_PWM',
pi.SERIAL:'Serial',
pi.UNKNOWN:'Unknown'}
return functions[pi.gpio_function(pin)]
## Future Functionality
## def setPullUp(self,pullup):
## """Defines the GPIO as having a pull up resistor so the input
## state is inverted when read
## setPullUp(True) - Pin is pulled up
## setPullUP(False) - Pin is not pulled up"""
## self.pullup = pullup
def toggleCmdState(self):
"""Reads the current state of the checkbox, updates LED widget
and sets the gpio port state."""
self.state = self.cmdState.get()
self.updateLED()
self.updatePin()
def updatePin(self):
"""Sets the GPIO port state to the current state"""
pi.output(self.pin,self.state)
def updateLED(self):
"""Refreshes the LED widget depending on the current state"""
self.led.set(self.state)
def updateInput(self):
"""Updates the current state if the pin is an input and sets the LED"""
if self.isInput():
state = pi.input(self.pin)
self.state = state
self.updateLED()
class App(Frame):
def __init__(self,parent=None, **kw):
Frame.__init__(self,parent,**kw)
self.parent = parent
pi.setmode(pi.BCM)
self.ports = []
## Get the RPI Hardware dependant list of GPIO
gpio = self.getRPIVersionGPIO()
for num,(p,r,c) in enumerate(gpio):
self.ports.append(GPIO(self,pin=p))
self.ports[-1].grid(row=r,column=c)
self.update()
def onClose(self):
"""This is used to run the Rpi.GPIO cleanup() method to return pins to be an input
and then destory the app and its parent."""
try:
pi.cleanup()
except RuntimeWarning as e:
print(e)
self.destroy()
self.parent.destroy()
def readStates(self):
"""Cycles through the assigned ports and updates them based on the GPIO input"""
for port in self.ports:
port.updateInput()
def update(self):
"""Runs every 100ms to update the state of the GPIO inputs"""
self.readStates()
self._timer = self.after(100,self.update)
def getRPIVersionGPIO(self):
"""Returns the GPIO hardware config for different Pi versions
Currently supports layout 1 and 3"""
gpio1 = ((0,0,0),
(1,1,0),
(4,2,0),
(17,3,0),
(21,4,0),
(22,5,0),
(10,6,0),
(9,7,0),
(11,8,0),
(14,0,1),
(15,1,1),
(18,2,1),
(23,3,1),
(24,4,1),
(25,5,1),
(8,6,1),
(7,7,1))
gpio2 = ((2,0,0),
(3,1,0),
(4,2,0),
(17,3,0),
(27,4,0),
(22,5,0),
(10,6,0),
(9,7,0),
(11,8,0),
(14,0,1),
(15,1,1),
(18,2,1),
(23,3,1),
(24,4,1),
(25,5,1),
(8,6,1),
(7,7,1))
gpio3 = ((2,0,0),
(3,1,0),
(4,2,0),
(17,3,0),
(27,4,0),
(22,5,0),
(10,6,0),
(9,7,0),
(11,8,0),
(5,9,0),
(6,10,0),
(13,11,0),
(19,12,0),
(26,13,0),
(14,0,1),
(15,1,1),
(18,2,1),
(23,3,1),
(24,4,1),
(25,5,1),
(8,6,1),
(7,7,1),
(12,8,1),
(16,9,1),
(20,10,1),
(21,11,1))
if pi.RPI_REVISION == 3:
gpio = gpio3
self.parent.title('Raspberry Pi GPIO - A+/B+/2B+')
elif pi.RPI_REVISION == 2:
#Change this when I know the pins on RPi GPIO Version 2
gpio = gpio2
self.parent.title('Raspberry Pi GPIO - A/B Rev2')
elif pi.RPI_REVISION == 1:
self.parent.title('Raspberry Pi GPIO - A/B')
gpio = gpio1
else:
self.parent.title('Raspberry Pi GPIO - Unknown Version')
##Assume same config as A+/B+/2B+
gpio = gpio3
return gpio
def main():
root = Tk()
root.title("Raspberry Pi GPIO")
a = App(root)
a.grid()
"""When the window is closed, run the onClose function."""
root.protocol("WM_DELETE_WINDOW",a.onClose)
root.resizable(False,False)
root.mainloop()
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
- Now save the program. We are saving it as gpio.py python file.
Step 2 - Running the program and Understanding the GUI panel
- Now open terminal and type command sudo python gpio.py to run the program.
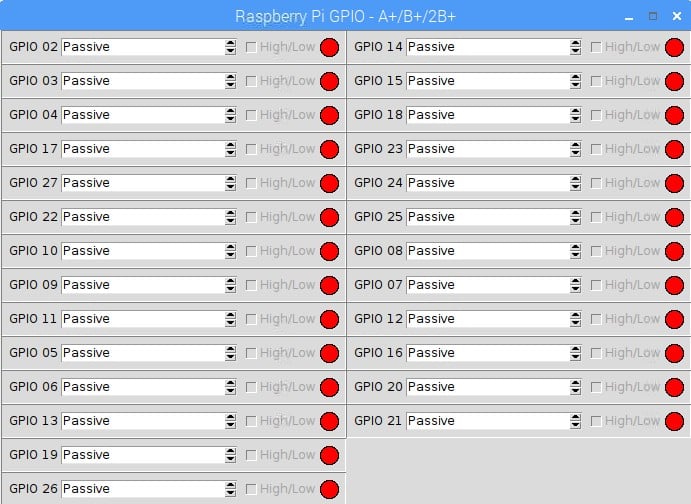
- A panel window will open up like this -
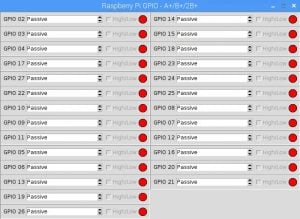
- From here you can set the status of any GPIO pin from the Corresponding drop down menu as Passive, Input or Output.
- If you have selected Output, then you will have to mark or unmark the corresponding High/Low box to make the Pin Low or High
- If you have selected Input, then the low Input will show the the Red colour and if input is high, it will show Green Colour.
Tags : Raspberry Pi Article