Types of Electric Motor and Uses – AC and DC Motor Explained Details
The electrical motor is the biggest advancements in the engineering and technology field ever since the invention of electricity.

In this 21st century without electricity, we can't imagine doing any of our jobs. There is a major development that happened in technology and civilization only after the introduction of electricity and electrical devices.
We can’t imagine our lives without ceiling fans, lights, computers, communication devices, and many more. It is proven that electricity and electrical devices play a major role in our lives, making them easier and more advanced.
One such piece of equipment that is continuously used in our domestic and industrial sectors is the electric motor. There are different varieties of motors used in different sectors according to their requirements. In this article, we are going to learn about the types of electric motors.
The electrical motor has been the biggest advancement in the engineering and technology fields ever since the invention of electricity.
What is an Electric Motor?
An electric motor is an electro-mechanical machine that converts electrical energy into mechanical energy. Basically, the motor produces the rotational force.
The working principle of the all-electric motor depends on the interaction between the magnetic and electric fields.
An electric motor has two types: the AC motor and the DC motor. Let’s see these types of electric motors in detail.
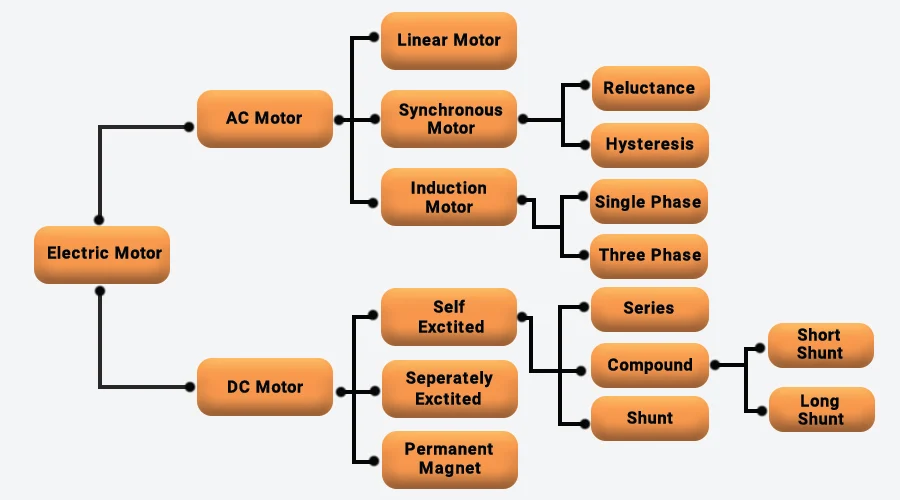
1. AC Motor
The AC motor requires an alternating current to rotate. This motor converts the alternating current into mechanical power using electromagnetic induction. The AC electric motor has two most important parts: the stator and the rotor.

The stator is the stationary part, and the rotor is the rotating part of the ac electric motor. Most AC motors are single-phase or three-phase.
The three-phase AC motor produces bulk power and is mostly used in industry. Single-phase AC motors are used in small power applications. The single-phase AC motor is small in size and used in a variety of services.
Most domestic appliances, such as refrigerators, fans, washing machines, and mixers, use a single-phase AC motor.
2. DC Motor
A motor that converts the DC power into mechanical power is referred to as a DC electric motor. It is operated by a DC current. The basic working principle of a DC motor is that when a current-carrying conductor is placed in a magnetic field, a force exerted on it develops torque.
The DC motor consists of two main parts: the armature and the stator. The rotating part is the armature, and the stationary part is the stator.

Types of AC Electric Motor
AC motors are mainly classified into three types, and they are:
- Synchronous Motor
- Asynchronous or Induction Motor
- Linear Motor
1. Synchronous Motor
The synchronous motor changes the alternating current into mechanical power at the desired frequency. In this motor, the speed of the motor is synchronized with the AC frequency. These motors mainly depend on the three-phase supply. In this, the motor speed is the constant speed at which the motor generates an electromotive force.

There is no air gap available in the speed of the stator current and rotor. So it provides more rotation accuracy. Because of high rotation accuracy, these motors are applicable in automation, robotics, etc.
The synchronous motor is segmented into two types:
(i) Reluctance Motor
The motor whose construction is similar to an induction motor and runs like a single-phase synchronous motor is called the reluctance motor.
In this motor, the rotor is like a squirrel cage, and the stator includes sets of windings such as the auxiliary and main windings. To offer a level operation at a stable speed, the auxiliary windings are very useful.
These motors are commonly used in signal generators, recorders, etc., which require proper synchronization.
(ii) Hysteresis Motor
The hysteresis motor has a uniform air gap and doesn’t have any DC excitation system. The rotor of this motor induces hysteresis and eddy current to complete its required task. The working of a motor depends on its construction, whether it is a single-phase or three-phase supply.
These motors provide very smooth operation with stable speed, similar to other synchronous motors. The noise level of this motor is quite small, and due to this reason, they are used in applications where soundproof motors are required like a sound player, audio recorder, etc.
2. Induction Motor
An induction motor or an asynchronous motor runs at an asynchronous speed. It uses electromagnetic induction to transform electric energy into mechanical power.

According to rotor construction, there are two types of induction motors. They are squirrel cage induction motors and phase wound induction motors.
On the basis of supply phases, the induction motor is classified into single-phase and three-phase induction motors.
(i) Squirrel Cage Rotor
The rotor of the motor has the shape of a squirrel cage. In this, the inner component is connected to the output shaft and looks like a cage. This rotor decreases the magnetic locking and the humming sound of the rotor.
(ii) Phase Wound Rotor
This rotor is a variation of the three-phase induction motor, which is designed to provide high torque for loads with high inertia while taking very little current. It is also known as slip ring motors.
(iii) Single-phase induction motor
The motor that converts single-phase AC electric energy into mechanical power by using electromagnetic induction is known as a single-phase induction motor.
(iv) Three-phase Induction Motor
The motor that converts 3-phase AC electric energy into mechanical power is known as a three-phase induction motor.
3. Linear Motor
A linear motor is an electric motor that has an unrolled stator and rotor. It produces a linear force along its length instead of a rotational torque. Linear motors are mostly used on sliding doors and in actuators.
Types of DC Electric Motor
As per the chart, based on its construction and electrical connection, the DC motor has different types.
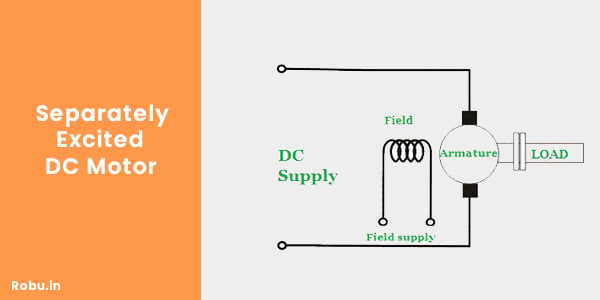
1. Separately Excited DC Motor
In this motor, the DC windings are excited by a separate DC source. The separate DC source energizes the armature windings of the motor; due to this, it produces the flux.
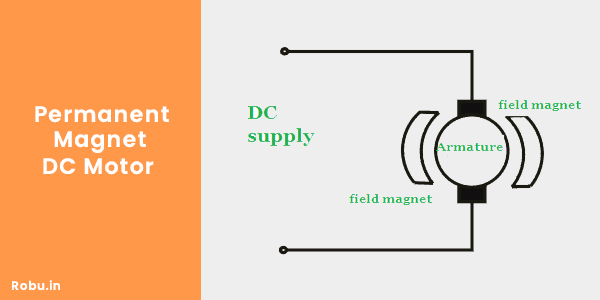
2. Permanent Magnet DC Motor
The motor that uses a permanent magnet to create field flux is a permanent magnet DC motor (PMDC).
The PMDC motor provides more starting torque and has very good speed regulation. However, it has limitations on torque, so they are typically found in low-power applications such as automobile starters, wipers, air conditioners, etc.
3. Self-Excited DC Motor
The motors in which the field winding is connected either in series or parallel to the armature winding is known as self-excited DC motors. Based on this, the self-excited DC motor is classified as:
(i) Series Wound DC motor
In a series-wound DC motor, the field winding connects in series with the armature of the motor.

(ii) Shunt Wound DC motor
In the shunt-wound DC motor, the field winding connects in parallel with the armature of the motor.
The shunt-wound motor offers good speed regulation. In this motor, the field winding can be separately excited or connected to the same source as the armature.

(iii) Compound Wound DC motor
The compound wound rotor has both parallel and series connections to the field winding. The excitation of a compound-wound DC motor has two types, depending on the nature of the compounding.

Cumulative compound DC motor: In this, the shunt field flux produced by the shunt winding assists the main field flux produced by the series winding.
Differential Compound DC Motor: In this, the shunt field flux diminishes the effect of the main series winding we can say that the motor
To understand the types of DC motors in detail, refer to the article Types of DC Motor.
Other Motors
There are different types of DC or AC motors available on the market with a variety of specifications, like stepper motors, servo motors, brushed DC motor, brushless DC motors, etc.
3. Stepper Motor
Stepper motors are also DC motors that divide a full rotation into a number of equal steps. They have multiple coils, and all are organized in groups called "phases".

This motor will rotate one step at a time by energizing each phase in sequence. Since each pulse helps the motor rotate at a precise angle, like 1.8°,
The motor position can be controlled without any feedback system. This motor provides very precise positioning and speed control. For this reason, stepper motors are used in many precision motion control applications. Stepper motors come in different sizes and electrical characteristics.
4. Servo Motor
A servo motor is a simple electric motor that rotates the machine parts with high efficiency and great precision. The servo motors are available in both AC and DC.

A servomotor is a linear or rotary actuator that allows for precise control of linear or angular position, velocity, and acceleration.
The servo motor uses a regular motor coupled with a sensor for positional feedback. It also requires a relatively sophisticated controller to operate.
Servo motors are used in many applications, like toy cars, RC helicopters and planes, Robotics, etc. To know more about it, refer to the article What is a servo motor?
Final Words
I hope this article helps you understand the detailed information about the types of electric motors. These electric motors are used in a number of applications. We hope that you found it interesting and that you will come back for more of our educational blogs.



I was a lecturer in a private University in Indonesia and Marine Engineering is my main interest. In my spare time I sometimes discuss (online) about some topics with my ex-student who become a manager in a shipyard now. At recent time, we discuss mostly about electricity, specifically marine electricity. Your article is very useful in widening my knowledge about electricity, so thank you so much. God Bless You always.
Best wishes,
Hadie Rijanto
Which DC motor is good for higher torque & How much Nm of torque that motor produces ?